Polarization in the standard X-ray band (a few keV) in astronomy is a window that had not been explored for more than 40 years since the 1970s, mainly due to the lack of high-sensitivity techniques. In 2001, a new technique for high-sensitivity X-ray polarimetry was demonstrated as possible in the INFN-Pisa laboratory and has been developed since then. The technique is based on the photoelectric effect and utilizes the gas pixel detector (GPD) to measure the 2D track of photoelectrons following the absorption of X-rays. As the photoelectric effect is the main interaction mechanism between X-rays and matters in this energy range, high-sensitivity X-ray polarimetry is enabled.
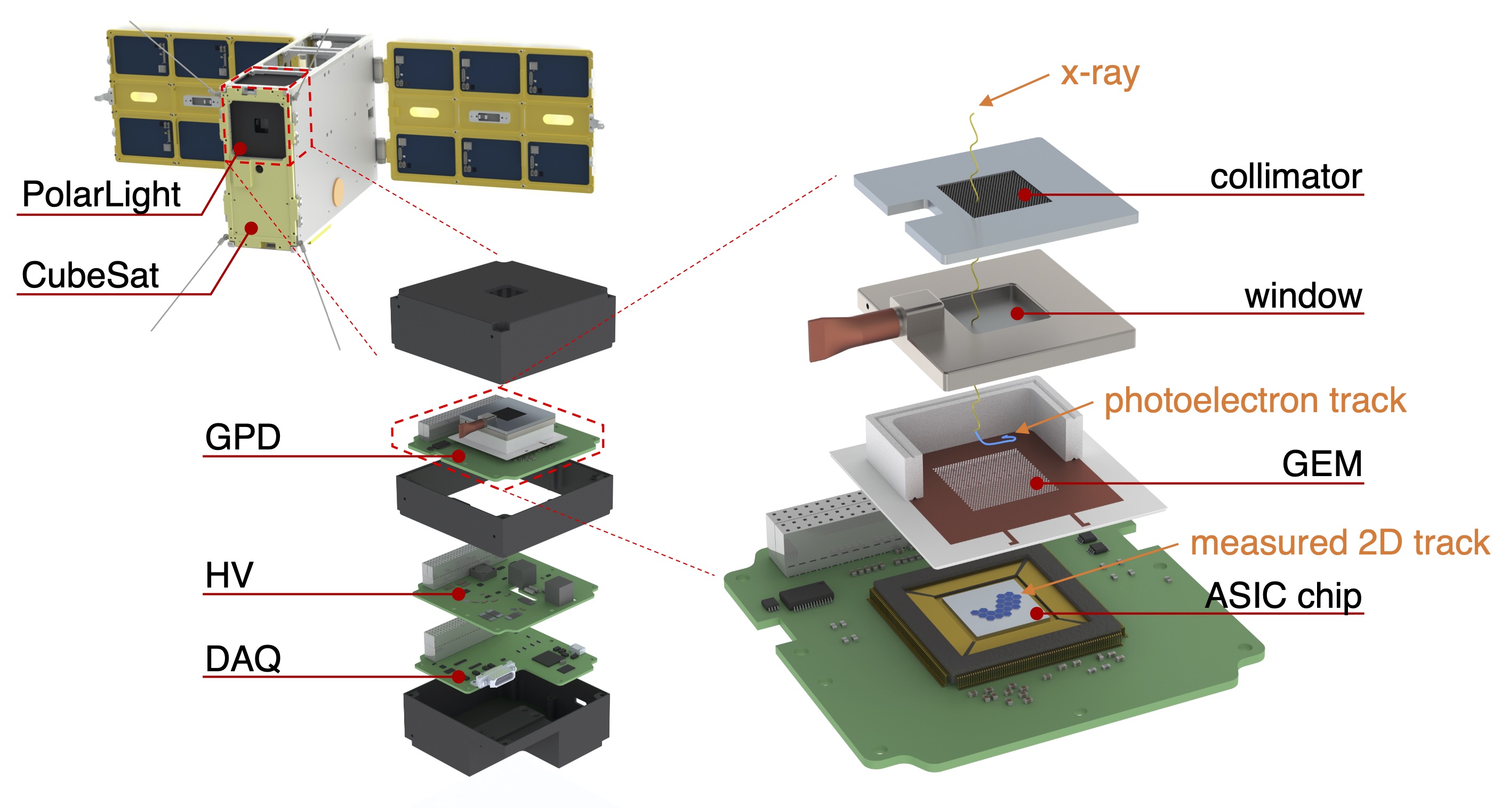
PolarLight is a compact soft X-ray polarimeter onboard a CubeSat, which was launched into a low-Earth orbit on 29 October 2018. The key component of PolarLight is the GPD, which is mounted on a printed circuit board, assisted with a high voltage (HV) board and a data acquisition board. The whole payload has a size of about 10 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm and occupies a standard unit (1U) of a CubeSat. PolarLight is the name of the payload, not the spacecraft. It shares the CubeSat "Tongchuan-1" with other payloads to lower the cost.
PolarLight is still functional in space by now. However, the data down-link is no longer available since February 2022. In the same month, we launched PolarLight-2, which is an improved version with a thinner entrance window (50 μm beryllium) and an on-line calibration source (Fe-55).
This project is a collaboration of Tsinghua, INFN-Pisa, INAF/IAPS-Rome, IHEP, Ningbo University of Technology, North Night Vision, and Spacety.
Papers related to PolarLight
- X-ray Polarimetry of the accreting pulsar 1A 0535+262 in the supercritical state with PolarLight
Long, X., Feng, H., Li, H. et al. 2023, ApJ, 950, 76
(Upper limits of the polarization degree obtained for a supercritical accreting pulsar, still lower than theoretical predictions)
- A significant detection of X-ray Polarization in Sco X-1 with PolarLight and constraints on the corona geometry
Long, X., Feng, H., Li, H. et al. 2022, ApJ, 924, L13
(Confirmed the marginal detection with OSO-8; favor the transition layer corona model and disfavor the accretion disk corona model)
- X-ray polarimetry of the Crab nebula with PolarLight: polarization recovery after the glitch and a secular position angle variation
Long, X., Feng, H., Li, H. et al. 2021, ApJ, 912, L28
(Follow-up observations of the Crab nebula measure a polarization angle inconsistent with that obtained with OSO-8)
- Discrimination of background events in the PolarLight X-ray polarimeter
Zhu, J., Li, H., Feng, H. et al. 2021, RAA, 21, 233
(A effective algorithm to distinguish source and background events)
- Modeling the in-orbit background of PolarLight
Huang, J., Feng, H., Li, H. et al. 2021, ApJ, 909, 104
(A particle tracking simulation of the orbital background with a mass model)
- In-orbit Operation and Performance of the CubeSat Soft X-ray Polarimeter PolarLight
Li, H., Long, X., Feng, H. et al. 2021, Advances in Space Research, 67, 708-714
(About the operation and in-orbit performance of the instrument)
- Re-detection and a possible time variation of soft X-ray polarization from the Crab
Feng, H., Li, H., Long, X. et al. 2020, Nature Astronomy, 4, 511
(The first scientific results with PolarLight)
- The X-ray polarimetry window reopens
Feng, H., and Bellazzini, R. 2020, Nature Astronomy, 4, 547
(An introduction to the experiment in the Mission Control column of Nature Astronomy)
- PolarLight: a CubeSat X-ray polarimeter based on the gas pixel detector
Feng, H., Jiang, W., Minuti, M. et al. 2019, Experimental Astronomy, 47, 225
(A detailed description of the mission profile)
- Electron track reconstruction and improved modulation for photoelectric X-ray polarimetry
Li, T., Zeng, M., Feng, H. et al. 2019, NIMA, 858, 62
(A new algorithm based on the graph theory is proposed for reconstruction of the electron track)
- Assembly and test of the gas pixel detector for X-ray polarimetry
Li, H., Feng, H., Muleri, F. et al. 2017, NIMA, 804, 155
(Description of the detector assembly and performance)
- Energy range: 2-8 keV
- Energy resolution: 19% @ 6 keV
- Field of view: 2.3° FWHM or 5.7° FWZR
- Weight: 580 g
- Power: 2.2 W
- Gas mixture: pure DME at 0.8 atm, 1 cm thick
- Window: 100 μm beryllium (50 μm for PolarLight-2)
- GEM: 100 μm pitch and 100 μm thick
- ASIC: 50 μm pitch
- Modulation factor: 0.42 @ 3.74 keV
Data archive for PolarLight
PolarLight (As of February 2022)
- Crab nebula: 1402 ks
- Sco X-1: 884 ks
- 1A 0535+262: 70 ks
- Background: 393 ks
PolarLight-2 is now monitoring the Crab nebula and Sco X-1 alternatively.
Schematic drawings of the CubeSat, PolarLight and its internal GPD. The right-hand side illustrates how a photoelectron track is measured following the absorption of an X-ray (adapted from Fig. 1 in Feng & Bellazzini 2020, Nature Astronomy, 4, 511).