Stars and Planets

—Exoplanets—
Chris Ormel

Roadmap module 2
Planets
what defines a planet; what type of planets are there in the solar system and in the exoplanet census
Kepler laws of planetary motion
the laws governing the motions of planets
Exo-Planet detection techniques
What are the mechanisms observers use to detect planets; what are their respective advantages and disadvantages; How to use them in order to assess the exoplanet census
- astrometry
- imaging
- microlensing
- radial velocity
- transits
What is a planet?
Definition. According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a planet is a celestial body which:
- is in orbit around the Sun; and
What is a planet?
Definition. According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a planet is a celestial body which:
- is in orbit around the Sun; and
- has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium (a nearly round shape); and
What is a planet?
Definition. According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a planet is a celestial body which:
- is in orbit around the Sun; and
- has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium (a nearly round shape); and
- has "cleared the neighborhood" around its orbit.
See IAU resolution B5

What is a planet?
Definition. According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a planet is a celestial body which:
- is in orbit around the Sun; and
- has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium (a nearly round shape); and
- has "cleared the neighborhood" around its orbit.
See IAU resolution B5
What is a planet?
Definition. According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a planet is a celestial body which:
- is in orbit around the Sun; and
- has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium (a nearly round shape); and
- has "cleared the neighborhood" around its orbit.
See IAU resolution B5
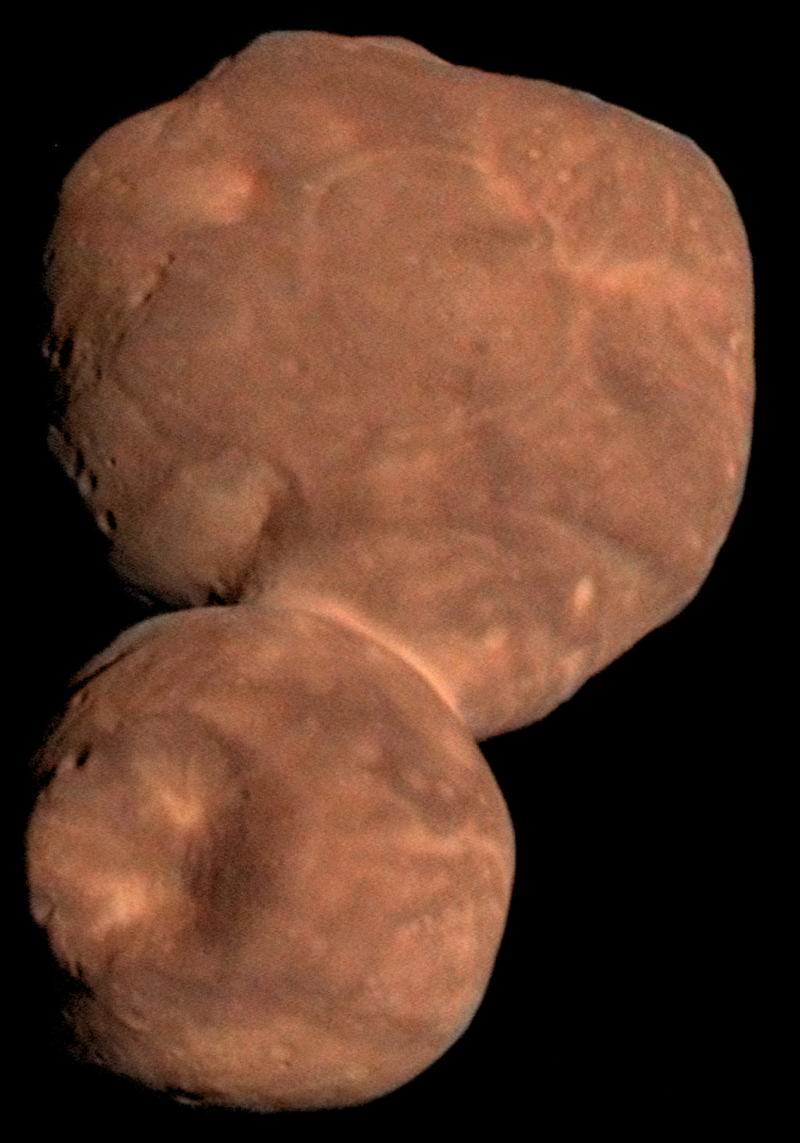
Ultima Thule Arrokoth — a Kuiper belt object (KBO)
What is a planet?
Definition. According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a planet is a celestial body which:
- is in orbit around the Sun; and
- has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium (a nearly round shape); and
- has "cleared the neighborhood" around its orbit.
See IAU resolution B5
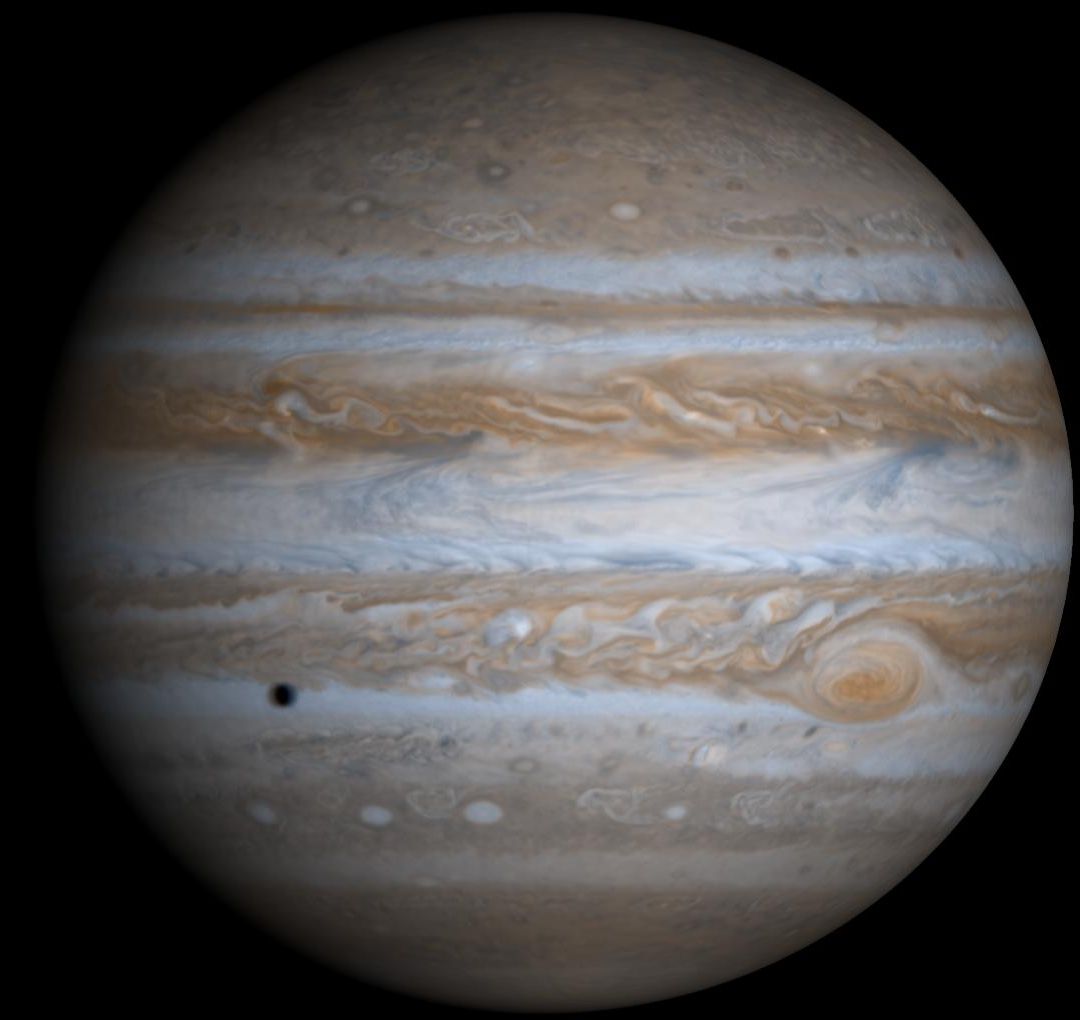
In the solar system, we distinguish:
- Giant Planets — consist primarily of hydrogen and helium
- Terrestrial Planets — consist primarily of "metals"
- Ice Giants — consist mostly of "metals" (ice+rock), but with large amounts of hydrogen and helium

What is a planet?
Definition. According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a planet is a celestial body which:
- is in orbit around the Sun; and
- has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium (a nearly round shape); and
- has "cleared the neighborhood" around its orbit.
See IAU resolution B5
In the solar system, we distinguish:
- Giant Planets — consist primarily of hydrogen and helium
- Terrestrial Planets — consist primarily of "metals"
- Ice Giants — consist mostly of "metals" (ice+rock), but with large amounts of hydrogen and helium

What is a planet?
Definition. According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a planet is a celestial body which:
- is in orbit around the Sun; and
- has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium (a nearly round shape); and
- has "cleared the neighborhood" around its orbit.
See IAU resolution B5
In the solar system, we distinguish:
- Giant Planets — consist primarily of hydrogen and helium
- Terrestrial Planets — consist primarily of "metals"
- Ice Giants — consist mostly of "metals" (ice+rock), but with large amounts of hydrogen and helium
Kepler's laws of planetary motion
read CO Ch 2.1
- motion follows an ellipse, with the Sun at one of its focii.
Non-interial reference frame (!)
- a line sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals:
![]()
- semi-major axis a and orbital period P are related as:
![]()
Here the constant equals
![]()
Laws can be understood from Newton's law of universal gravitation:

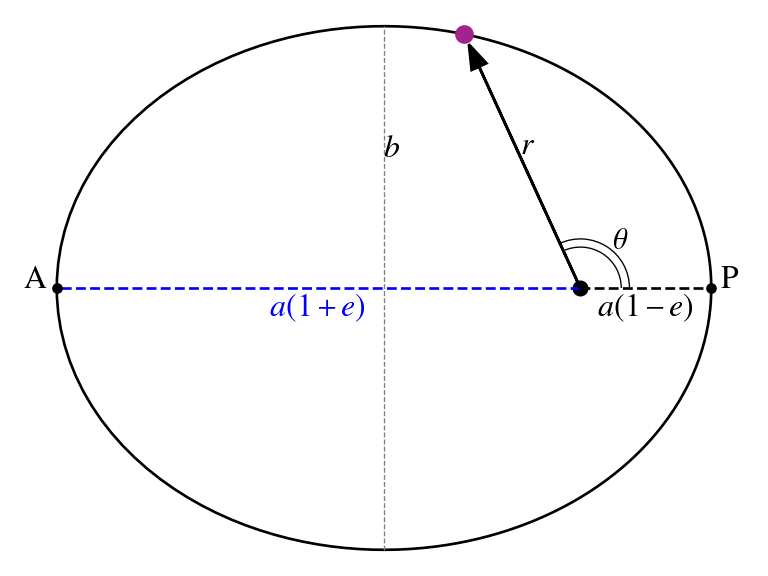
Geometry of the orbit: The particle follows elliptical motion, in which the Sun is located at one of its focii (The other one is empty.) The orbit is given by:

(To be derived in M7.Two body problem)
Exoplanet dection techniques — Astrometry
Astrometry is another indirect planet detection technique. It measures the angular motion of nearby stars across the sky. This motion consists of three components (which?) :
- the proper motion of the star through the galaxy
- the motion of the Earth around the Sun (parallax)
- the deviation caused by the gravitational perturbation from companions (e.g., planets)
Presently, few planets have been detected with astrometry, but this is going to change with GAIA
Exoplanet dection techniques — Astrometry

Astrometry is another indirect planet detection technique. It measures the angular motion of nearby stars across the sky. This motion consists of three components (which?) :
- the proper motion of the star through the galaxy
- the motion of the Earth around the Sun (parallax)
- the deviation caused by the gravitational perturbation from companions (e.g., planets)
Presently, few planets have been detected with astrometry, but this is going to change with GAIA
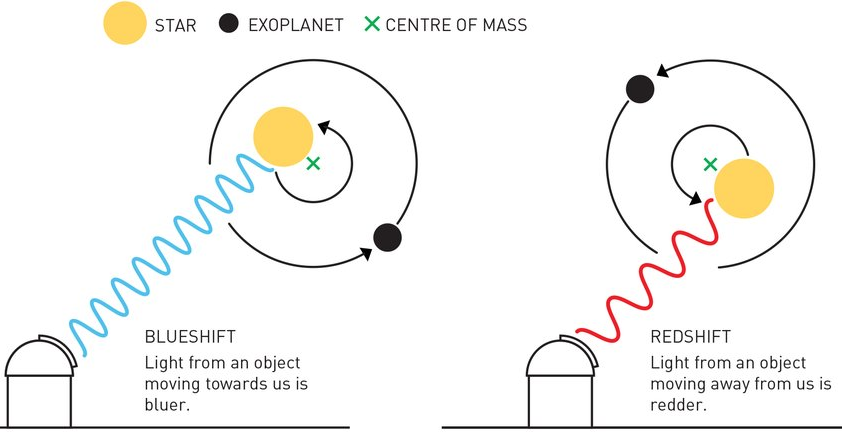
Radial velocity method (Doppler spectroscopy)
Radial velocity method (Doppler spectroscopy)
The method employs two concepts:
- Center of mass at 0:
![]()
- Kepler's 3rd law:
![]()
where:
![]() P is period,
a semi-major axis,
G Newton's constant
P is period,
a semi-major axis,
G Newton's constant
Assume that
 then:
then:

the quantities on the RHS can be measured (P,
 or can be assumed
or can be assumed

From the Doppler technique one actually gets only the radial velocity component of the star
 Hence, this detection method is known as the
radial velocity (RV) method.
Hence, this detection method is known as the
radial velocity (RV) method.
Radial velocity method (Doppler spectroscopy)
The method employs two concepts:
- Center of mass at 0:
![]()
- Kepler's 3rd law:
![]()
where:
![]() P is period,
a semi-major axis,
G Newton's constant
P is period,
a semi-major axis,
G Newton's constant
Assume that
 then:
then:

the quantities on the RHS can be measured (P,
 or can be assumed
or can be assumed

From the Doppler technique one actually gets only the radial velocity component of the star
 Hence, this detection method is known as the
radial velocity (RV) method.
Hence, this detection method is known as the
radial velocity (RV) method.
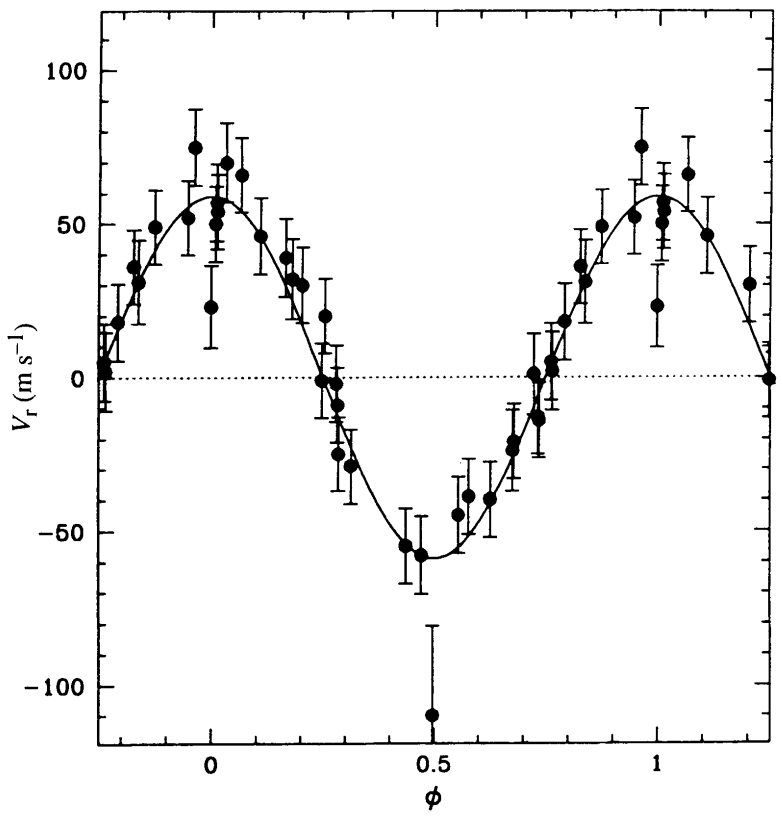
Radial velocity method (Doppler spectroscopy)


Radial velocity method (Doppler spectroscopy)

Question — The RV method is best suited to detect massive planets on orbits close to the parent star
- What is an issue with this technique to discover small planets like the Earth at 1 au?
- What is an issue for observing Jupiter-mass planets at Jupiter's orbit (5.2 au) with this technique?



Nobel Prize
— in Physics —



| year | winners | topic |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | L'Huillier, Krausz, Agostini | attosecond pulses |
| 2022 | Aspect, Clauser, Zeilinger | quantum information science |
| 2021 | Manabe, Hasselmann, Parisi | climate modelling, fluctuations in physical systems |
| 2020 | Penrose, Genzel, Ghez | predictions black hole formation and discovery of supermassive BH at center galaxy |
| 2019 | Peebles, Mayor, Queloz | contributions to our understanding of the evolution of the universe and Earth's place in the cosmos |
| 2018 | Ashkin, Mourou, Strickland | method of generating high-intensity, ultra-short optical pulses |
| 2017 | Weiss, Barish, Thorne | decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves |
| 2016 | Thouless, Haldane, Kosterlitz | theoretical discoveries of topological phase transitions and topological phases of matter |
| 2015 | Kajita, McDonald | Discovery of neutrino oscillations, which shows that neutrinos have mass |
| 2014 | Asaki, Amano, Nakamura | invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources |
| 2013 | Englert, Higgs | Higgs particle |
| 2012 | Haroche, Wineland | ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems |
| 2011 | Perlmutter, Schmidt, Riess | discovery of the accelerating expansion of the Universe through observations of distant supernovae |



Nobel Prize
— in Physics —



| year | winners | topic |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | L'Huillier, Krausz, Agostini | attosecond pulses |
| 2022 | Aspect, Clauser, Zeilinger | quantum information science |
| 2021 | Manabe, Hasselmann, Parisi | climate modelling, fluctuations in physical systems |
| 2020 | Penrose, Genzel, Ghez | predictions black hole formation and discovery of supermassive BH at center galaxy |
| 2019 | Peebles, Mayor, Queloz | contributions to our understanding of the evolution of the universe and Earth's place in the cosmos |
| 2018 | Ashkin, Mourou, Strickland | method of generating high-intensity, ultra-short optical pulses |
| 2017 | Weiss, Barish, Thorne | decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves |
| 2016 | Thouless, Haldane, Kosterlitz | theoretical discoveries of topological phase transitions and topological phases of matter |
| 2015 | Kajita, McDonald | Discovery of neutrino oscillations, which shows that neutrinos have mass |
| 2014 | Asaki, Amano, Nakamura | invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources |
| 2013 | Englert, Higgs | Higgs particle |
| 2012 | Haroche, Wineland | ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems |
| 2011 | Perlmutter, Schmidt, Riess | discovery of the accelerating expansion of the Universe through observations of distant supernovae |
In recent years 5/13 Physics Nobel prizes have been awarded to Astronomy/Astrophysics!
Transit method
- The idea of finding planets through transits is straightforward: The planet reduces the brightness of the star by a small amount.
- This amount ("transit depth") is proportional to the size of the planet
- In 1999 the first "transiting planet" was detected.
Transit method
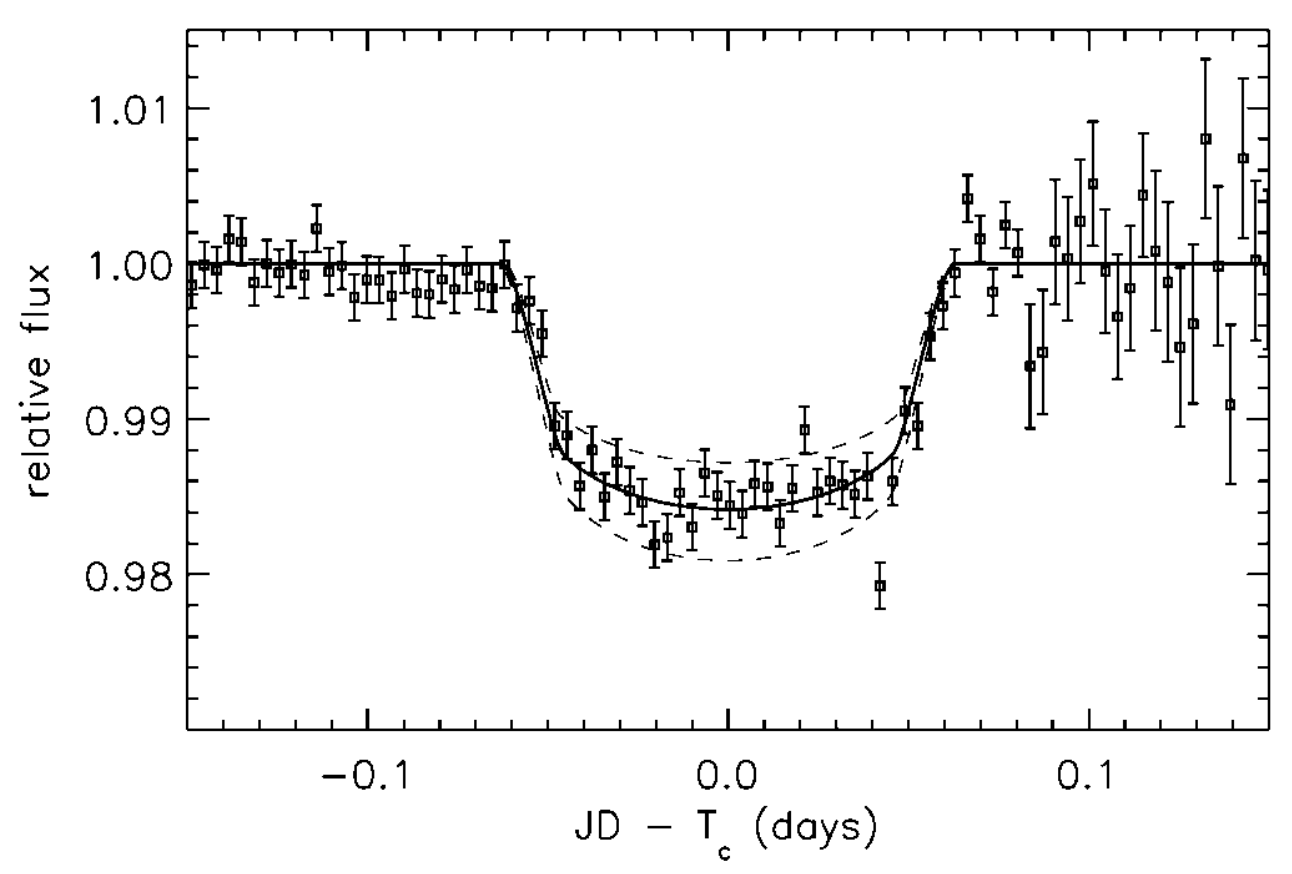

- The idea of finding planets through transits is straightforward: The planet reduces the brightness of the star by a small amount.
- This amount ("transit depth") is proportional to the size of the planet
- In 1999 the first "transiting planet" was detected.
Transit method

detecting thousands of exoplanets
by looking at a small region of the sky.

is finding many planets around bright star
across the entire sky.
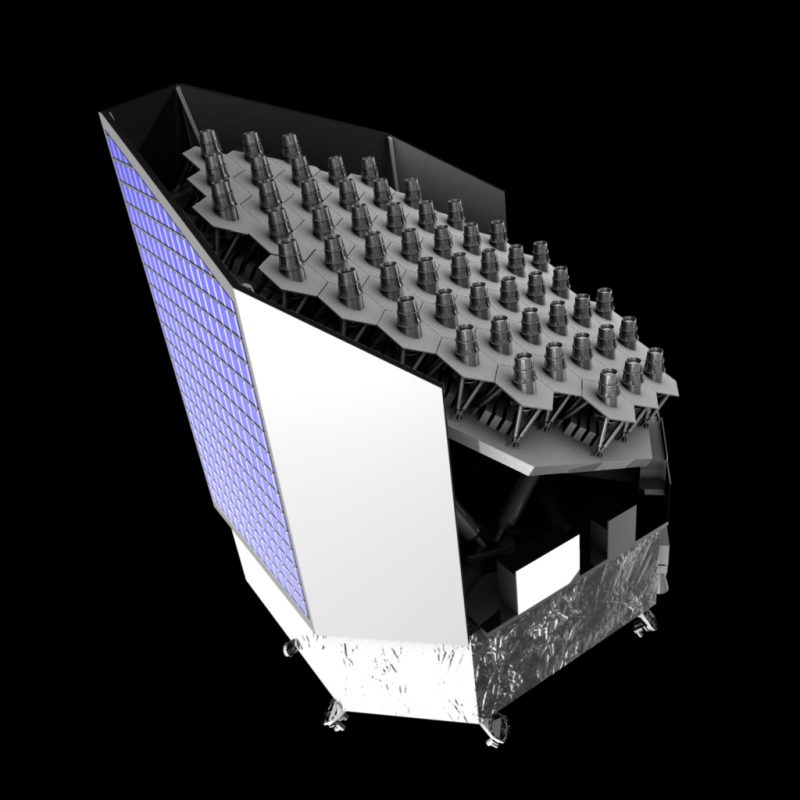
will be launched around 2026 by ESA.
Target: Earth-like planets in habitable zone.
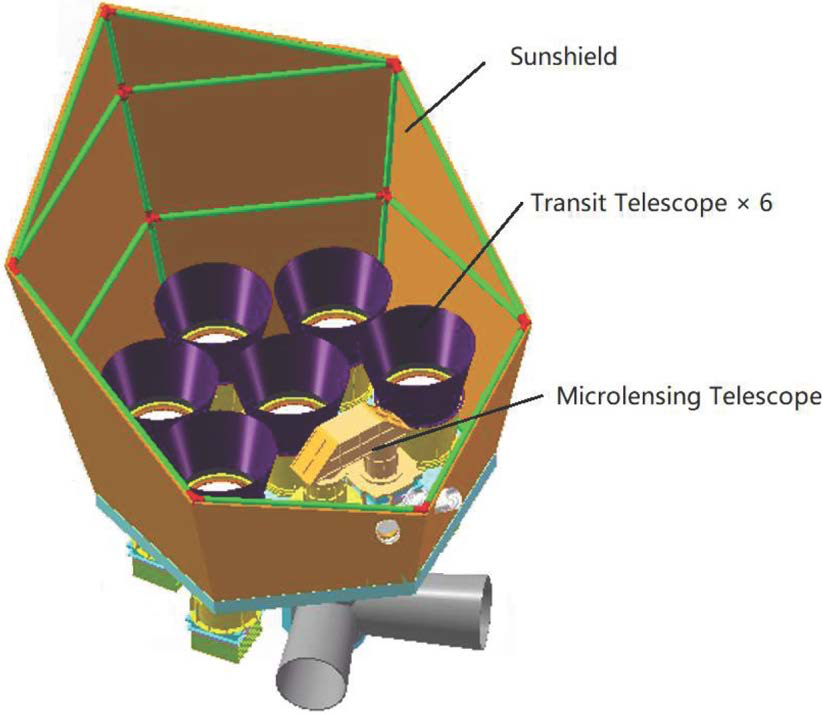
mission
- The idea of finding planets through transits is straightforward: The planet reduces the brightness of the star by a small amount.
- This amount ("transit depth") is proportional to the size of the planet
- In 1999 the first "transiting planet" was detected.
- Space missions as Kepler, TESS and in the future Plato, Earth2.0 will discover many exoplanets through transits
Microlensing
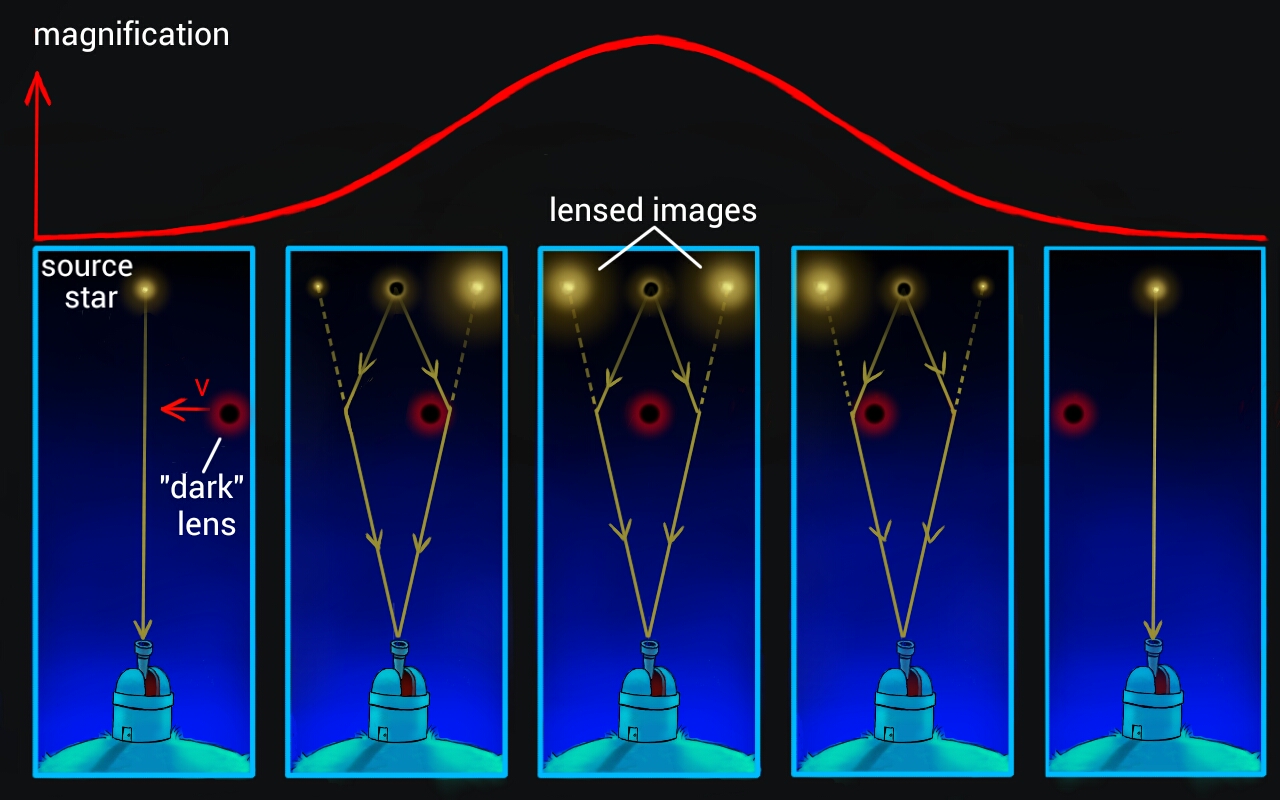
Microlensing
Microlensing
 into the direction of the observer O.
into the direction of the observer O.
 and
and
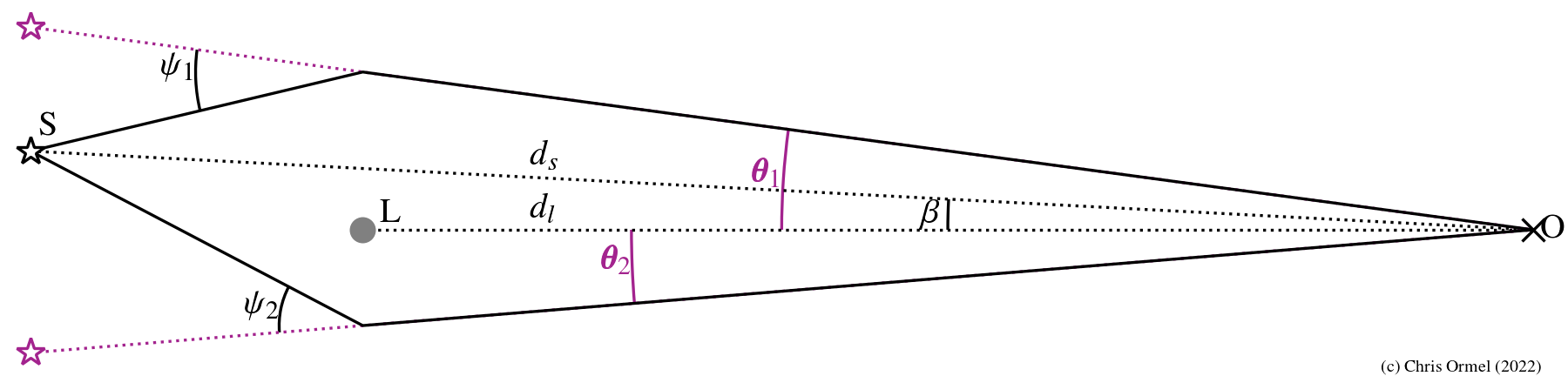
 are the distances to the source and the lens, respectively.
In reality all angles are very small.
are the distances to the source and the lens, respectively.
In reality all angles are very small.
Microlensing
 ,
,
 , and
, and
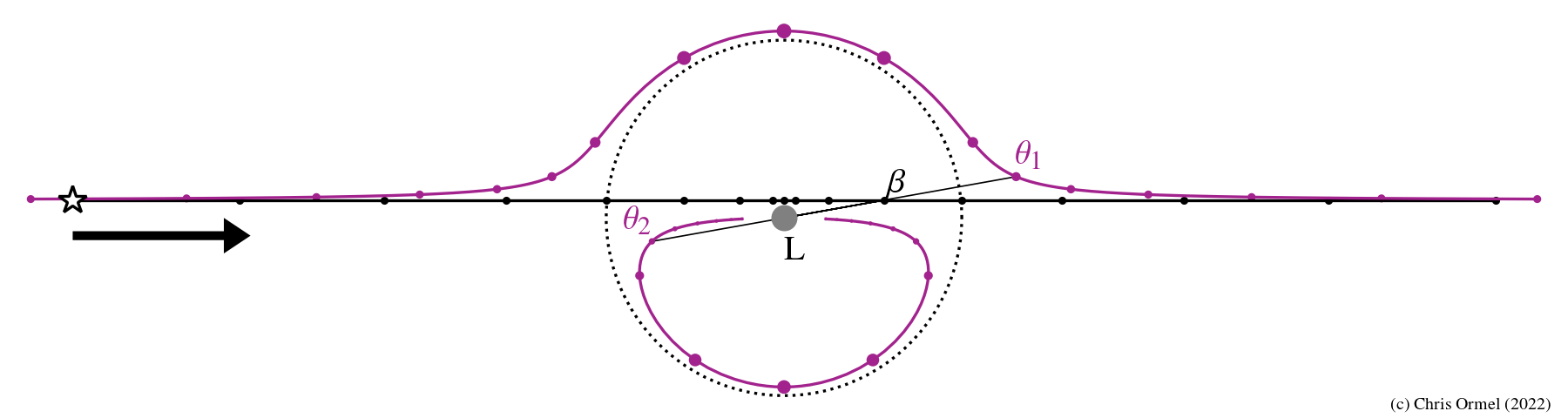
 lie on the same line.
lie on the same line.

Microlensing

 ,
,
 , and
, and
 lie on the same line.
lie on the same line.

 into the direction of the observer O.
into the direction of the observer O.
 and
and
 are the distances to the source and the lens, respectively.
In reality all angles are very small.
are the distances to the source and the lens, respectively.
In reality all angles are very small.
In (micro)lensing light from a background star is gravitationally deflected by foreground lens.
- The amount of deflection is governed by the Lens equation:
![]()
where
![]() is the between the source and the
lens, and
is the between the source and the
lens, and
![]() is the
Einstein radius:
is the
Einstein radius:
![]()
- The lensing results in a magnification of the background star by a factor
![]()
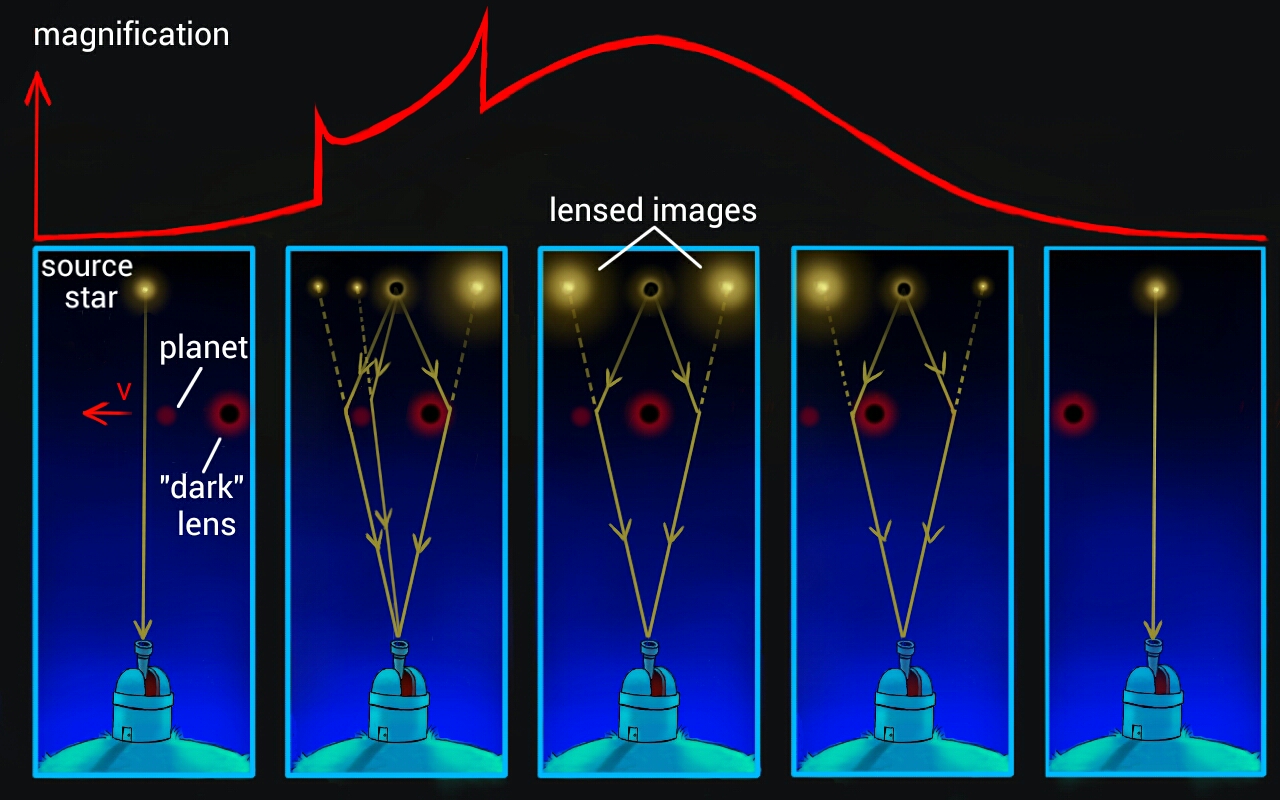
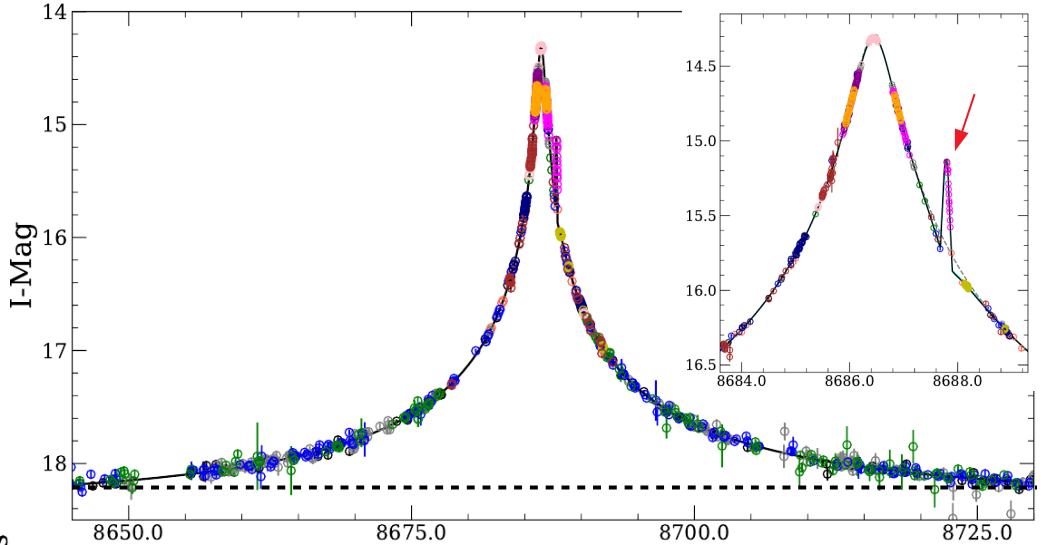
The magnification is therefore greatest near the Einstein ring. A planet in the lens plane may alter the lightcurve, however.
Microlensing

In (micro)lensing light from a background star is gravitationally deflected by foreground lens.
- The amount of deflection is governed by the Lens equation:
![]()
- The lensing results in a magnification of the background star by a factor
![]()
- A planet P in the lens plane affects the magnification profile.
Direct Imaging
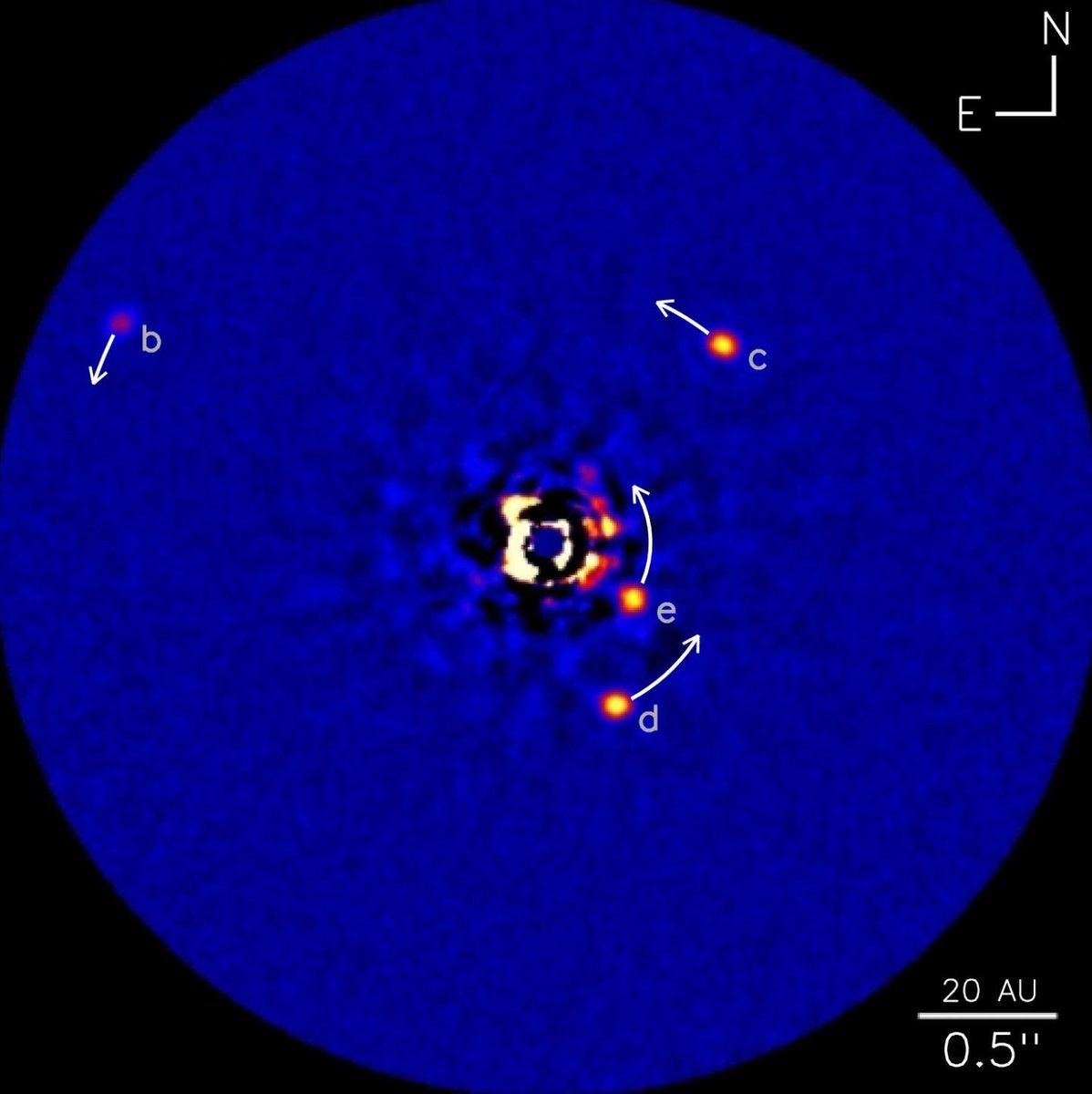

Direct imaging techniques use a coronagraph (takes out the stellar light). It works best when:
- planets are young and bright
- planets are far from the star
Direct Imaging
Direct imaging techniques use a coronagraph (takes out the stellar light). It works best when:
- planets are young and bright
- planets are far from the star
end of module 2
—congrats—















